AWS
Lambda
- serverless functions that run on demand in response to events, such as:
- updates to application state, like a user putting an item in their shopping cart
- on demand via HTTP requests
- changes to #Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets
- table updates in #DynamoDB
- state transitions in #Step Functions
- you only pay for used compute time
- smaller functions are better because they're faster to cold start (start up in a brand new container)
- containers stick around for a bit after finishing, if the function runs again in this container this is a warm start
- some people schedule lambdas to run every few minutes to ensure warm starts, #SST has built-in cronjobs to do this
- code around the actual lambda function will only run once per container start, this can be used to setup things like database connections
- integrates with other AWS services - ex. pull files from S3 buckets
- can use any third-party library, natively supports many languages (including Node)
- code and dependencies are packaged and uploaded to an S3 bucket
- there is a limit on the total package size, if you need larger you can use a Docker image
Amplify
- full stack application hosting (similar to Vercel)
- zero config for Next.js and Nuxt
- fully typed configuration, similar to #SST
- supports SSR, SPAs, static apps, and native or Flutter/RN mobile apps
- integrates with other AWS services
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
- non-serverless cloud computing infrastructure platform
- servers are virtualized and can be spun up and terminated as needed
- paid for by the second
- useful for web hosting, though simple static pages can be hosted on S3
Simple Storage Service (S3)
- key-value cloud object storage
- objects: files + metadata
- buckets: containers for objects
- can be used to host files (including static web pages) for public access, not just access from other S3 services
- offers versioning, replication across regions, per-object permissions with IAM
- data lake: stores data in its original form, relational or non-relational
- schema-on-read: the data schema doesn't need to be defined until it's read
- S3 Glacier: meant for archiving data that's rarely accessed, cheaper storage prices but higher data access costs
- also has even cheaper plans with slower retrieval times (minutes-hours instead of milliseconds)
Aurora
- MySQL and PostgreSQL compatible relational database
DynamoDB
- serverless NoSQL database
- key-value and document data models
- don't need to worry about updates, maintenance, manual scaling, etc.
- global tables: replicated across multiple regions, can read and write to any replica
- DynamoDB Streams - capture every change so that event-driven applications can respond to them
- continuous (per-second) or on-demand backups, encrypted at rest
Redshift
- SQL data warehouse solution
- data warehouse: stores relational data in a concrete schema (schema-on-write)
- harder to scale than a data lake
Elasticache
- Redis or Memcached caching
CloudFront
- CDN with edge caching
Route 53
- DNS and domain name management
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
- distributes traffic across multiple zones or servers (don't have to be AWS services)
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- traffic filtering, can protect against things like SQL injection and XSS
API Gateway
- lets you create and manage APIs (HTTP, REST or WebSocket) that call #Lambda functions or HTTP endpoints
- HTTP APIs are cheaper, but don't support some features of REST APIs, like edge optimization and API key management
- manages traffic, CORS, authorization and access control, throttling, monitoring, version management
Simple Queue Service (SQS)
- message queue
- pull-based - consumers pick messages out of the queue at their own speed
- supports both standard queues (messages may be delivered out of order or more than once) or FIFO queues (guarantees messages are delivered in order and exactly once)
- while a message is being processed, it's hidden from other requests for the duration of the user-set visibility timeout (default 30 seconds)
- it's the responsibility of a message consumer to delete the message once it's done processing, otherwise it will go back in the queue for other consumers to try
Other message services
- Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): lets messages be sent to multiple subscribers through topics
- uses a push model - good when immediate response is needed, such as real-time user engagement or alarm systems
- doesn't hold messages if subscribers are offline
- SNS messages can be sent to a SQS queue to offer both immediate delivery and persistence
- Amazon MQ: for migrating from existing message brokers like RabbitMQ
Identity and access management (IAM)
- fine-grained permissions system used across AWS products
- can define different roles with different permissions
Cognito
- user directory and authentication server
- two components:
- user pools: for authorizing users of your app or API
- identity pools: for authorizing users to access your AWS resources
- you can have a user sign in to a user pool to authenticate them, then exchange a user pool token with the identity pool to get credentials for AWS services
- can assign IAM roles based on rules or group membership in the user pool
- you can also offer custom authentication, or no authentication (for anonymous access)
- you can have a user sign in to a user pool to authenticate them, then exchange a user pool token with the identity pool to get credentials for AWS services
CloudFormation
- infrastructure as code tool for managing resources across AWS services
- resources are organized into "stacks", which can be created from templates
- stacks are region-specific
Step Functions
- visual programming (like Power Automate or UE Blueprints) for distributed applications
- example use cases:
- automate ETL (data ingestion/transformation) pipelines
- orchestrate multiple #Lambda functions into microservices
- process large datasets in parallel
- create workflows for security incident response
Frameworks
SST
- third-party tool for setting up and deploying full-stack apps easily on AWS (and other cloud providers)
- infrastructure as TypeScript code
- supports various frontends (Next.js, Astro, Solid), cronjobs, storage buckets, databases, queues, and more
- lets you run your lambdas locally for development and debugging
Serverless Framework
- similar to SST, but YAML-based
- serverless-http lets you use Express and other API frameworks with serverless, by translating incoming request payloads into an Express-compatible format
- since it's still serverless, you can't use state that persists between requests
Architecture examples
Web hosting
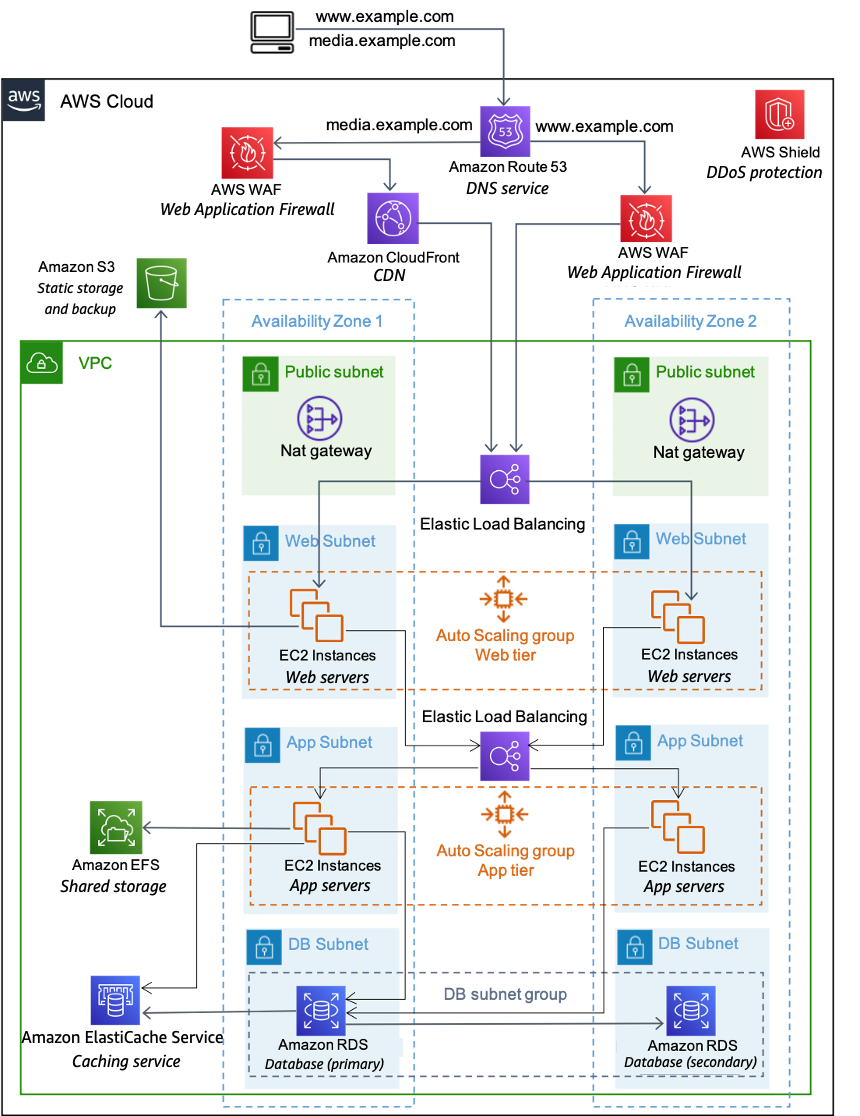
An AWS Cloud architecture for web hosting - Web Application Hosting in the AWS Cloud
Troubleshooting
Delete stuck CloudFormation stack
-
If you get a Failed to delete stack: Role {role} is invalid or cannot be assumed error when trying to delete a stack:
-
create a new role with type AWS Service, use case CloudFormation, permission AdministratorAccess, with the name of the role the stuck stack used (the part after
:role/) -
may take a few seconds for the role to propagate to CloudFormation
-
if there are any resources left in the Resources tab that were already deleted (such as a Lambda function), try the delete again and check the box to retain them
Export Route 53 DNS zonefile using cli53
cli53 export --full --debug example.com > example.com.zone 2> example.com.zone.log